Traumatic Brain Injury: Treating Problems and Preventing Further Damage
Personal Injury Attorneys | Traumatic brain injury is a term often used to describe injuries sustained by our soldiers in combat zones, but traumatic brain injury can occur from other situations. Researchers are finding new ways to treat traumatic brain injury to minimize damage and allow patients to manage symptoms.
What Is Traumatic Brain Injury?
Traumatic brain injury occurs when the brain suffers a bump, blow, severe jolt or penetrating wound that injures tissue inside the cranial cavity. When the head suffers a hard blow, the brain can hit the bony cavity of the skill, bruising and damaging brain tissue. Penetrating wounds can tear and even remove tissue causing severe trauma to the brain. Injuries can range from minor to severe, and cause a variety of effects.
Causes of Traumatic Brain Injury
Combat injuries are only one cause of traumatic brain injuries. Falls account for up to 35.2 percent of traumatic brain injuries. Automobile accidents account for another 17.3 percent. Ten percent of traumatic brain injuries are caused by physical assaults. Sports activities often cause concussions, which as also a type of traumatic brain injury. Any injury to the head should be looked at by a medical professional to ensure that brain injury has not occurred.
Symptoms of TBI
Symptoms related to traumatic brain injury can range from mild to severe. The patient may have lost consciousness for seconds or minutes at the time of injury. He may complain of headaches, lightheadedness, dizziness, confusion, blurred vision, eye fatigue, ringing in ears or lethargy. Behavioral or mood changes can occur with TBI. Changes in sleep patterns may also be evident. Severe injury can cause paralysis or coma.
Diagnosis of Traumatic Brain Injury
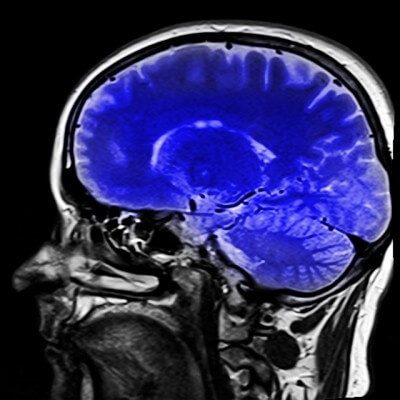
Accidents that cause brain damage often require quick diagnosis in order to minimize damage and begin treatment. Physicians and other medical personnel generally use the Glasgow Coma Scale to assess the initial brain injury. This test uses 15 points to numerically score symptoms of injury, such as ability to process and follow directions, eye and limb movements, speech coherence and other factors. Information about the injury and its severity can also help physicians determine the amount of damage that has occurred. Computerized tomography, or CT scans, provide cross-sectional images of brain tissue to detect injuries. Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, produces 3-D images of brain tissue that can show where damage has occurred. A probe may also be inserted in the brain cavity to measure intracranial pressure. Mild forms of injury to the brain can be difficult to diagnose.
Treatments for TBI
Mild brain injuries may not require any treatment at all, other than rest and pain relievers to treat headache. For severe injuries, medical treatment should begin as soon as possible after injury. The physician may administer diuretics to reduce fluid in tissues and reduce swelling in the brain. Anti-seizure drugs may be given to prevent further injury to brain tissues. Coma-inducing drugs are sometimes given to allow oxygen and nutrients to flow to the brain tissues. About half of the patients with traumatic brain injury will require surgery to remove or repair ruptured blood vessels or bruised tissue in the brain. Sometimes, fractures of the skull need repair or a window may be cut in the skull to relieve pressure on the brain.
Prognosis for TBI Patients
Disability from traumatic brain injury can vary greatly depending on the severity of the damage, the location of the damage, and the age and general health of the individual. Problems with thinking, reasoning and memory can remain. Sensory processing, such as sight, hearing, touch, taste and smell can be affected. Behavioral problems or mental health issues may remain, such as continued depression, anxiety or aggression. Severe brain injury can cause the person to remain in a persistent vegetative state. Some symptoms can be alleviated with medications and therapy. – Heil Law
The employment discrimination lawyers at Printy Law Firm can inform you of legal options you may not know you have. If you or a loved one has experienced an injury or wrongful death due to someone else’s negligence, contact The Personal Injury Department at Printy Law Firm.
Call today for a confidential consultation | Tampa 813.434.0649 | Tallahassee 850.877.7299